Lecture 1.2: Hash Pointers and Data Structures
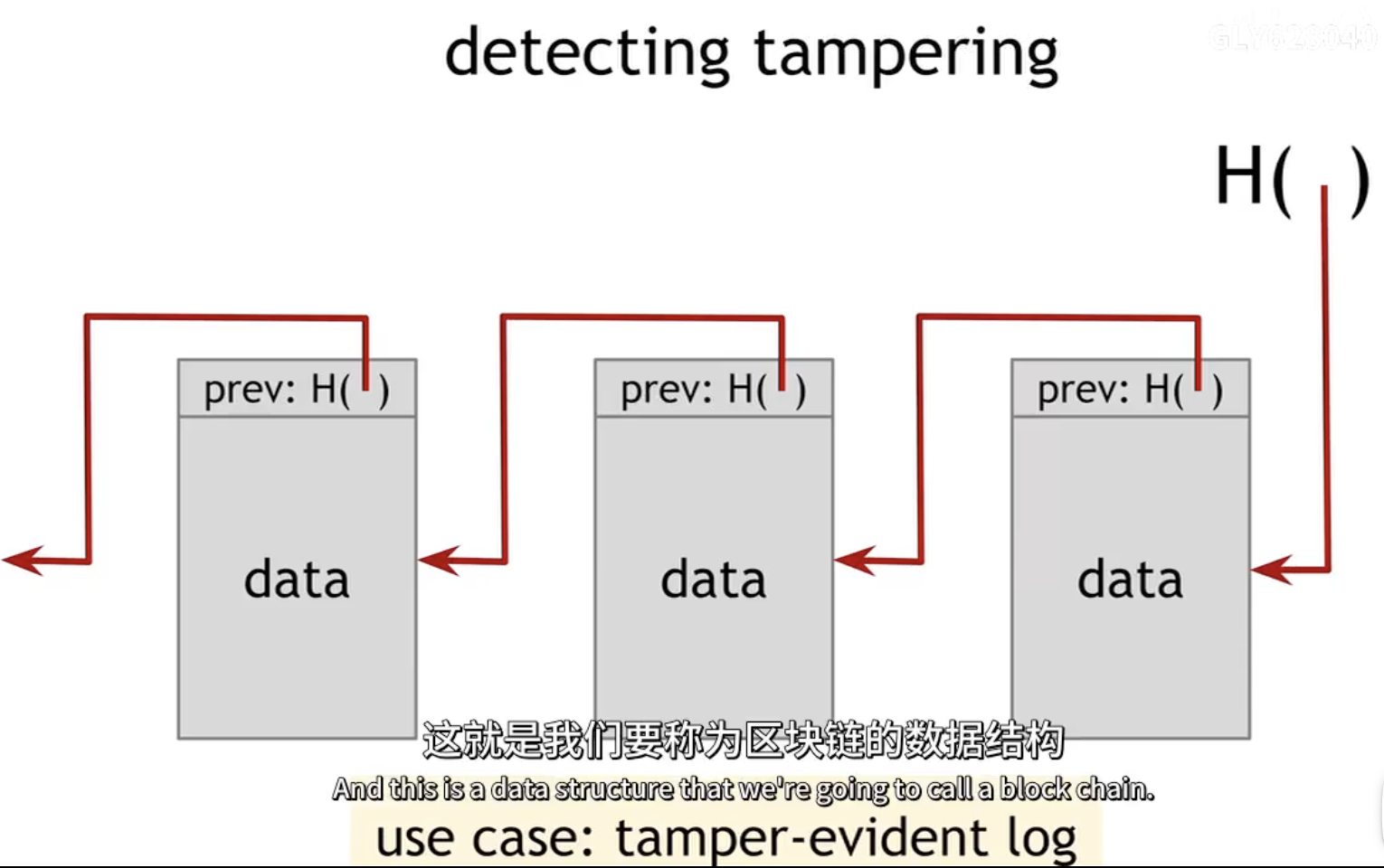
block chain:
Have a series of blocks,
each block has data as well as a pointer to the previous block in ths list,
here the previous block pointer will be replaced with a hash pointer.
If the adversary wants to tamper with data anywhere in this entire chain, in order to keep the story consistent, he’s going to have to tamper with hash pointers all the way back to the beginning.
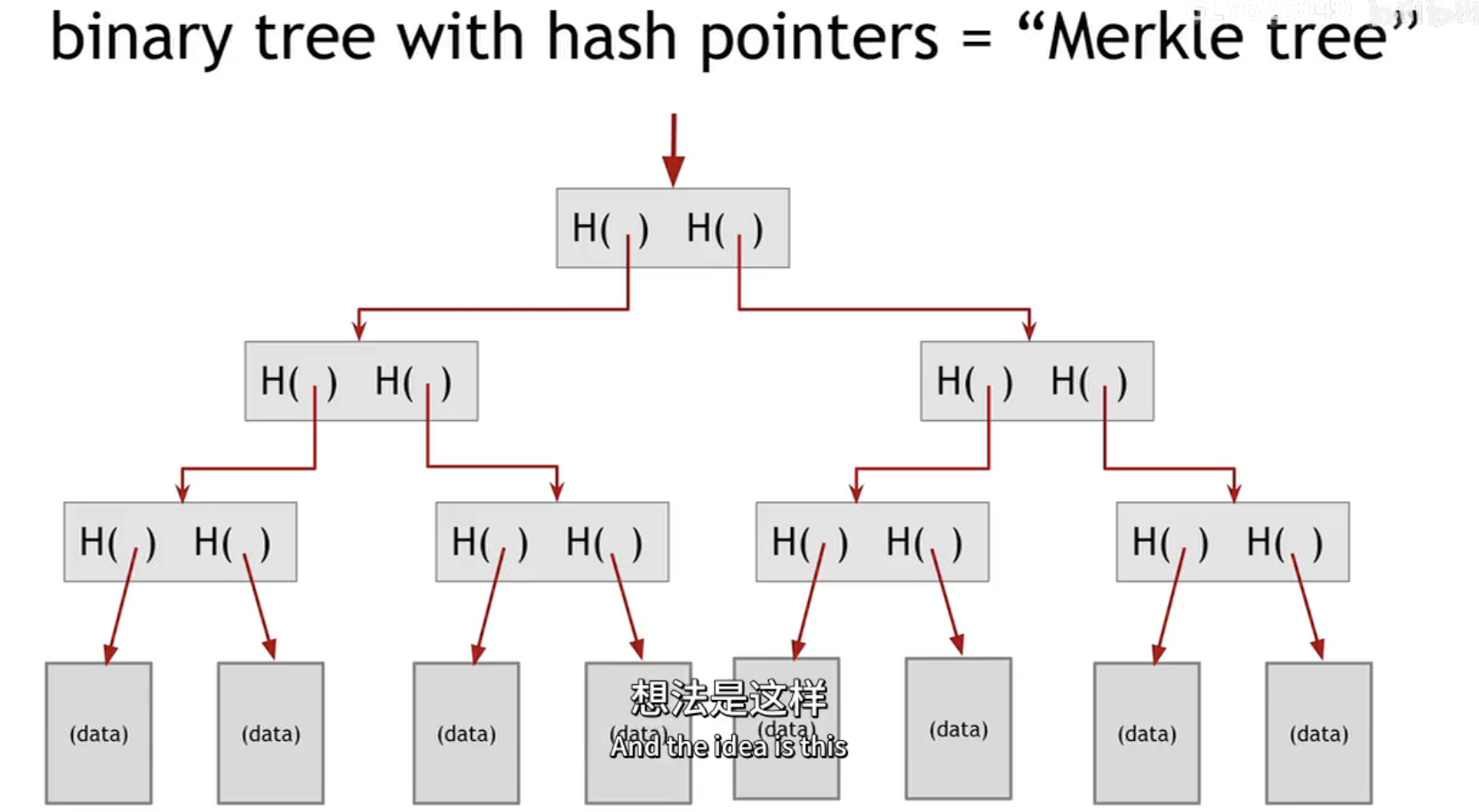
Merkle tree
Binary tree with hash pointers
In this case, if someone wants to prove to us that a particular data block is a member of this Merkle tree, all they need to show us, is this amount of data:
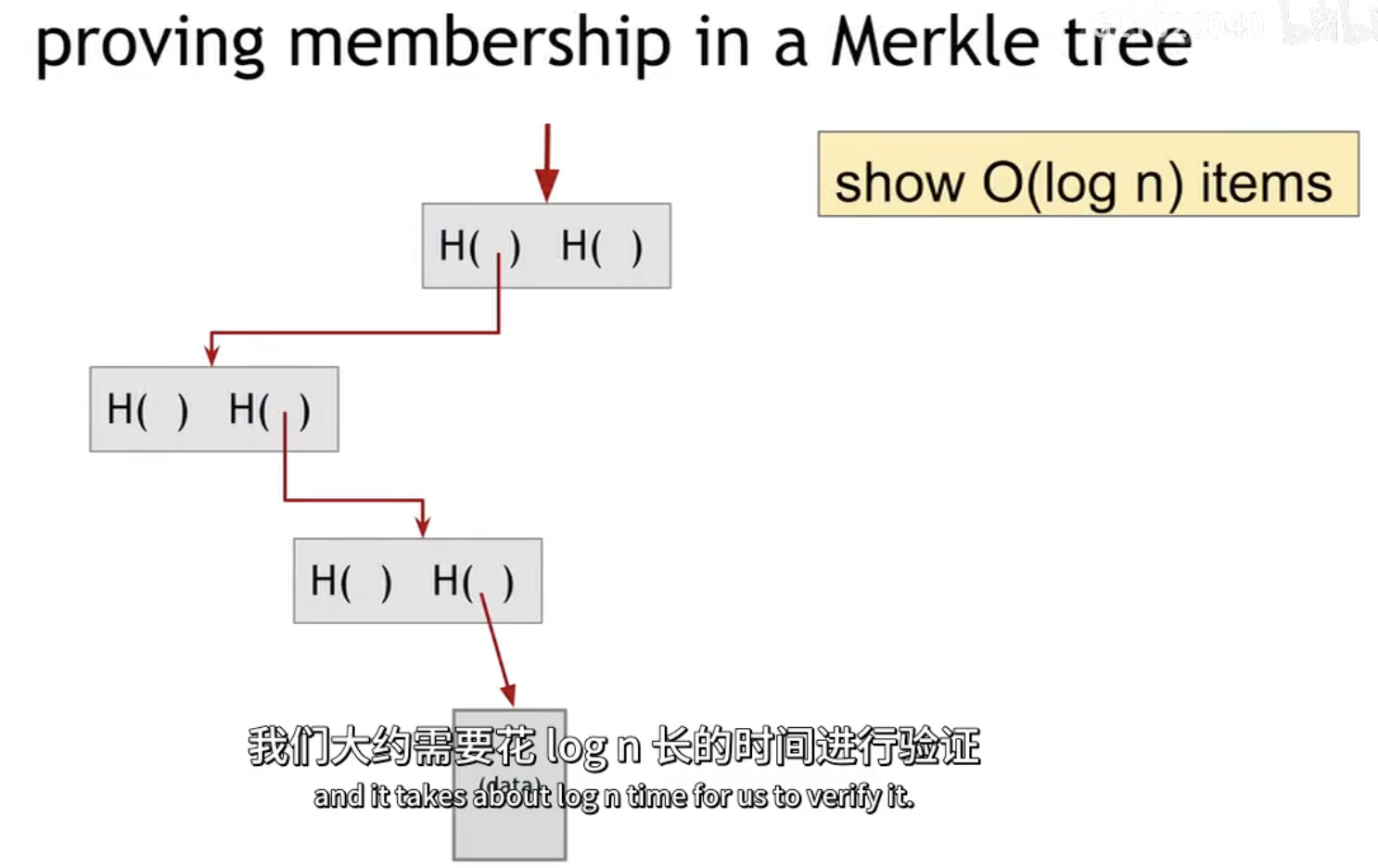
it takes about $log(n)$ time for us to verify it. It means that we can verify proven membership in a relatively short time at a very large number of blocks.